Article 2 Of Uniform Commercial Code
Article 2 Of Uniform Commercial Code - Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. Our collection aims to show each section of the u.c.c. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Allocation or division of risks. That means we will not always display. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily.
Allocation or division of risks. That means we will not always display. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. Our collection aims to show each section of the u.c.c. Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”).
Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily. Allocation or division of risks. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Our collection aims to show each section of the u.c.c. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. That means we will not always display.
UNIFORM COMMERCIAL CODE ARTICLE 1 GENERAL
Our collection aims to show each section of the u.c.c. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code.
revision of uniform commercial code article 1
Our collection aims to show each section of the u.c.c. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Article 2 of the ucc is a code that.
Uniform Commercial Code 20102011 Ed
Allocation or division of risks. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Our collection aims to.
An Overview of Article 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code and its Role in
Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily. That means we will not always display. Allocation or division of risks. The.
REVISION OF UNIFORM COMMERCIAL CODE ARTICLE 9
Allocation or division of risks. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. That means we will not always display. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform.
Uniform Commercial Code Article 9 Update — Report Lorman Education
Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.”.
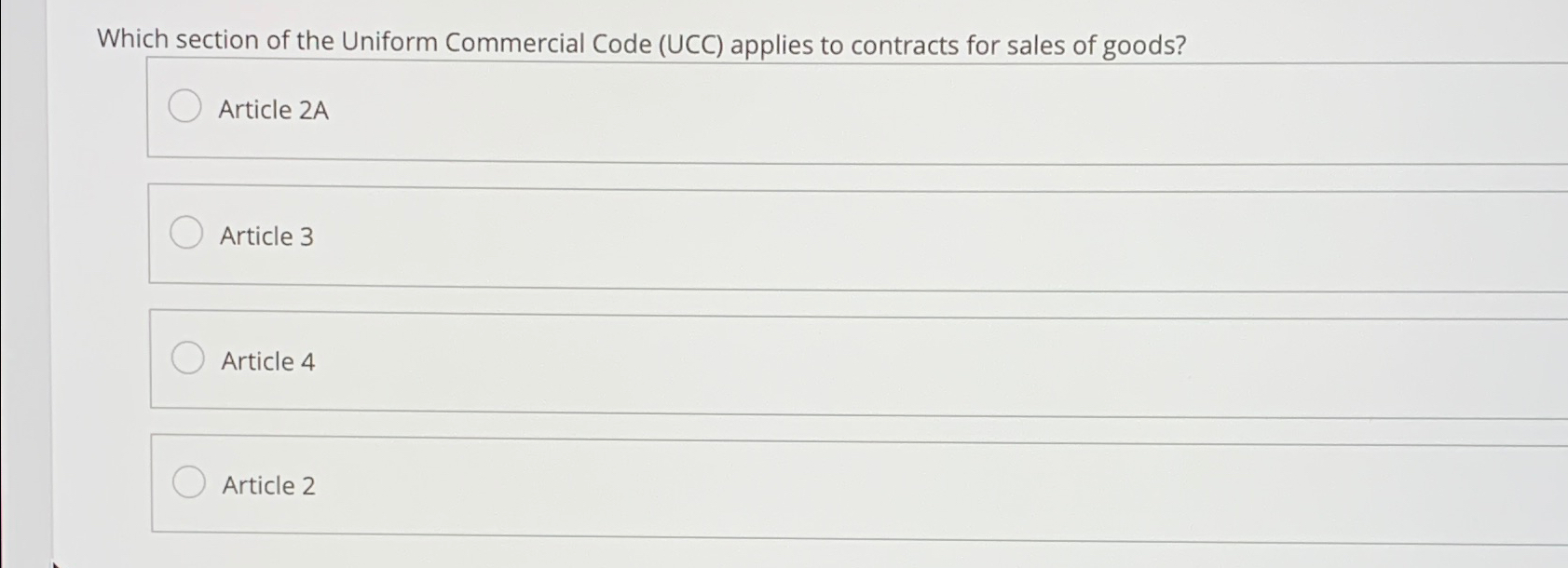
Solved Which section of the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC)
The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily. That means we will not always display. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time.
UNIFORM COMMERCIAL CODE Stop the Pirates of Commercial Sea.pdf DocDroid
Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). In the version which is most widely adopted by states. Article 2 of the ucc is a code that.
The uniform commercial code made easy pdf garetdeli
That means we will not always display. Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. Allocation or division of risks. Our collection aims to show each section of the u.c.c. In the version which is most widely adopted by states.
Report on Article 9 of the Uniform Commercial Code
Allocation or division of risks. In the version which is most widely adopted by states. That means we will not always display. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”). Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception).
Our Collection Aims To Show Each Section Of The U.c.c.
Article 2 defines goods as “all things that are movable at the time of identification to the contract for sale.” this includes tangible, movable. That means we will not always display. Allocation or division of risks. The answers to these questions are generally governed by article 2 of the uniform commercial code (“ucc”).
In The Version Which Is Most Widely Adopted By States.
Article 2 of the ucc is a code that governs transactions for goods, which most states (louisiana being the major exception) have statutorily.